“Khonsu: The Wanderer of Moon Magic in Ancient Egypt”
In ancient Egypt, the God Khonsu was known as the moon deity. The name “Khonsu” means “The Wanderer”. Moon magic was an important topic in ancient Egypt, and it played a central role in the magical system, which was based on the lunar calendar.
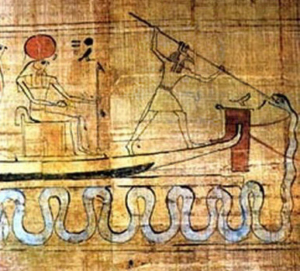
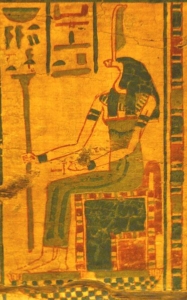
The Egyptian Moon God Khonsu
Khonsu, the wanderer of moon magic in ancient Egypt, being a Lunar deity, is not the only one, for the ancient Egyptians this would be the first month of Summer which is also where some of us are now. In the Egyptian tongue or the late version of it, the word is Pachons which you can break down into an Egyptian phrase per-en-khonsu “ the one of Khonsu” which can be contracted to Pachons.
In the Egyptian worldview, each month of the lunar cycle was dedicated to a specific deity, as exemplified by the month of Khonsu. While some deities were replaced or lost over time, the original concept remains: every month, throughout the seasons, holds special significance for a particular deity. Khonsu, the moon god, continues to be honoured in this lunar month.
Moon Magic

The Wanderer is an obvious reference to the moon’s fast-moving and irregular cycle. Egyptian Luna deities are, I would say, invariably male. Other examples would be Horus and Set. This shows, as people have long recognized, that there’s no simple equation of males being solar and females being lunar, which is sometimes heard within the Neo-Pagan Theology and other theologies as well. Perhaps the metaphor of male and female as plus and minus, maybe you’d say for the Egyptians that wasn’t quite as important. It wasn’t the only way that they represented this important idea of a binary relationship between things.
Within Egyptian culture, a binary relationship between a pair of gods is a very important motif. But it doesn’t necessarily mean that they have to be male and female. It’s an option but there are other ways of showing the same thing. And just to confuse things even more, the categories of male and female are a little bit more flexible within the Egyptian system and it would be possible to find a male lunar deity who has what is usually thought of as female attributes such as the capacity to “give birth”.
As Set gives birth to Thoth, one Moon God gives birth to another. This is a very interesting piece of mythology which we probably have to go into sometime, but we’ll leave that for now, because it’s such a rich area. As I said, this interplay of important principles often uses sexual metaphors but they can be male/female male/male or female/female and other counterparts and there can also be a sexual aspect that is just not the kind of strict male / female modality, which for them was not the only game in town.
Quite a lot of interactions between the Egyptian gods are between those nominally of the same gender, male and male or female and female and the homoerotic aspect of that was not avoided by the Egyptians it’s just not thought to be anything you always had to comment on. Or they may have seen it as just part of life as far as they were concerned. So for instance the sun god Ra, the nocturnal sun can be another way of referring to the Moon. In this mythology, the nocturnal sun, the Sun at midnight, is the Moon. And he has an important union to consummate with another underworld deity, the lord of the dead or Osiris. And when they come together and form a new entity, there’s a kind of sexual frisson to it, which they just didn’t feel that they had to comment on.
Conclusion:
Khonsu, a lunar deity, marks the beginning of summer for ancient Egyptians, a concept preserved in the term “Pachons.” This aligns with the Egyptian belief that each lunar month is dedicated to a specific deity, exemplified by Khonsu’s enduring connection as the moon god. The epithet “The Wanderer” references the moon’s dynamic cycle, with Egyptian lunar deities predominantly portrayed as male, like Horus and Set. This defies the simplistic notion of males as solar and females as lunar, challenging binary interpretations in theology. Egyptian culture embraces fluidity in gender and deity attributes, allowing for male lunar deities with traditionally feminine traits. This complexity extends to mythology, where interactions between deities transcend gender norms, including homoerotic undertones, as seen in Ra’s nocturnal guise symbolizing the moon. Explore the multifaceted nature of Egyptian theology, where the interplay of gods reflects a rich tapestry of symbolism and meaning.
More on Khonsu (Videos) :
The Wandering Moon
The Wanderer, Khonsu Moon