
In a world that often celebrates the power of individualism, there’s a quiet force reshaping the way we seek knowledge and guidance: collective wisdom. Just as ecosystems flourish through the harmony of diverse species, communities thrive when people share their experiences and insights. Each voice, like a note in a symphony, adds depth and resonance, creating a melody of wisdom far richer than any solo performance.
Consider how ideas come alive in collaboration spaces—whether in brainstorming sessions, online forums, or community gatherings. These interactions reveal a treasure trove of wisdom where perspectives don’t merely align but inspire new ways of thinking. Here, the collective becomes a living library of experience, offering lessons and insights that no single “guru” could provide alone.
This dynamic challenges us to rethink what it means to learn and grow. It invites us to step into both the roles of teacher and student, sharing our journeys and supporting each other in an environment that values every voice. In this dance of shared understanding, we find the true essence of mastery—not in isolated enlightenment but through the rich, interconnected exploration of life’s path.
‘The Collective is the Guru’ is a series of essays created for the Amookos group, exploring the evolving concept of the guru and collective wisdom. Each essay will spotlight a different teacher who has shaped and inspired the group.
One of the teachers who has greatly influenced my journey is John Power Power, also known as Sri Vilasanath.
John Power bridges Eastern and Western esoteric traditions, blending tantra, surrealism, and introspective art. As head of the Uttara Kaula Fellowship, he promotes mental liberation through creative enjoyment, drawing on his roots in both tantric spirituality and countercultural movements like the 1960s Gandalf’s Garden magazine. His work spans various media, including exhibitions and books that explore symbolism, mysticism, and the divine feminine. Power’s teachings invite us to embrace a path of mystical insight and personal freedom.
To better understand the origins and development of the Uttara Kaula tantric tradition’s revival, I reached out to John Power, also known as Sri Vilasanath, the leader of the Uttara Kaula Fellowship. He has been instrumental in bringing this North Indian spiritual lineage into a modern East-West context, shaping it as a bridge between traditional tantra and Western spirituality. In this interview, Power shares insights on how the fellowship was adapted for contemporary seekers worldwide.
I’ve asked John to share his journey into spirituality and esoteric studies, detailing how it led him to explore Tantra and Shaktism.
Here’s what he had to say:
“I would like to begin by noting that the development of an Indian tradition like Uttarakaula to include international exponents could only have emerged from the mid-1960s era known as Psychedelia. Some viewed this period as colourful and socially liberating, while others took the mind-expanding implications of the era’s name more seriously. I fall into the latter category, having been interested in philosophy and psychology since my school days.
After school, I attended art school, but after a year, I decided to drop out. I realised I had made the mistake of studying commercial art, which I found served the purpose of persuading people to spend money they didn’t have on things they didn’t need. Instead, I chose to take my portfolio of psychedelic drawings to the emerging alternative magazine offices in ‘Swinging London.’
While visiting a traditional studio where a friend worked, she introduced me to a magazine called “Gandalf’s Garden,” subtitled “The Mystical Scene Magazine.” J.R.R. Tolkien’s works have become widely popular, often associated with children’s fantasy adventures, which appealed to the hippies of that era. However, the magazine that borrowed the name of a Tolkien character contained serious articles more aligned with its subtitle, “Mystical Scene Magazine.” This set it apart from other counterculture magazines emerging at the time, as it was less politically focused.
When editor Muz Murray saw the drawings, he was pleased with what he found. As a result, my then-wife Chris and I moved to a crash pad/office in Ladbroke Grove, West London, where I worked on magazine layout and illustration. As the flat became too crowded, Chris and I relocated to the Garden Shoppe and wholefood café at the far end of Kings Road in Chelsea, where we slept in the cellar. During the day, Chris worked in the shop, while I cycled back to the office to continue working on the magazine. On Friday nights, the cellar was transformed into a Moot, hosting various Indian yogis, occasional yoginis, Druids, and anyone with an interesting agenda that Muz knew. The room would fill with young hippies and other interested parties eager to listen and contribute.
The only compensation for our work was food and shelter. Our financial support came from the DHSS. Eventually, I had to take a job with a friend from my art school days in Colchester, where he was operating a silk screen printing studio. Chris found a job in a boutique. Despite our busy schedules, we maintained contact with the Gardeners.
A friend named Sam worked on a farm, and during the winter when there was less work, he would often travel abroad, usually to India. While there, he met an Englishman named Nik Douglas, who had recently written a book titled “Tantra Yoga,” as well as other works on the subject later on. This was the first book I read about ‘Tantra’ and its connection to Indian mysticism.
When Nik was in London with his partner and their young child, we visited them a few times after they converted an old warehouse into a home. On one occasion, Nik showed us a film he had made to visually document the concepts presented in his book; this film can still be found on YouTube. It was funded by Mick Jagger, and interestingly, the Rolling Stones’ logo features a depiction of Kali’s tongue!
Sam also brought back clothes, trinkets, and reading materials from India. Among the reading materials was a magazine edited by an ex-pat Scotsman named John Spiers, who lived in Kerala, South India. The magazine focused on various mystical philosophies. It featured articles by another expatriate from England, Mahendranath, known as Dadaji to his followers in Gujarat, which is further north in India. I began a correspondence with both men.
Dadaji had previously published two articles in Nik Douglas’ magazine, ‘Chakra,’ before the publication of ‘Values.’ He was also the same person who later invited Mike Magee to his hermitage in Gujarat and initiated him into the Adi Nath Sampradaya. This invitation followed their exchange of magazines through a small press exchange, during which Dadaji discovered that Mike was involved in the OTO, although it was not the same OTO Dadaji had known during his time in England. Nonetheless, he encouraged Mike to start the East-West magical group known as AMOOKOS. Dadaji advised me to contact Mike, so I did, and I met him and Jan in Golders Green, North London. We discussed how to implement Dadaji’s planned ideas for his legacy.
Mike was well-connected because he publicised the magazine ‘Sothis’. When Dadaji’s essays began arriving in large numbers, it was mainly Mike’s responsibility to start publishing them. He left Kenneth Grant’s Typhonian OTO to dedicate more time to Nath Publishing. Later, he wrote the grade papers for AMOOKOS and also contributed to a smaller magazine called ‘Azoth’, which focused on similar topics. Meanwhile, I worked on another small magazine known as ‘Phoenix’.
Mike’s friends in England and the U.S. soon reprinted the essays or began to write texts inspired by them. However, there were early signs that Dadaji’s health and memory were declining due to his age, although he had not admitted any problems to anyone. This led to confusion and issues, as one person would work on a task Dadaji had assigned, only for another to discover a different and contradictory plan. An example of this occurred when Mike compiled the grade papers into a book later titled “Tantra Magick.” Dadaji claimed he hadn’t approved the book, yet he had received rough drafts that he likely hadn’t read.
At one point, when similar issues had arisen, Dadaji surprised me on my 30th birthday by presenting me with a charter to establish a Western, East-West form of a Shakta-centered Tantric group based on the Uttarakaula lineage that Pagalababa of Ranchi, India, had bequeathed to Dadaji. If this was intended to annoy Mike, it certainly succeeded!
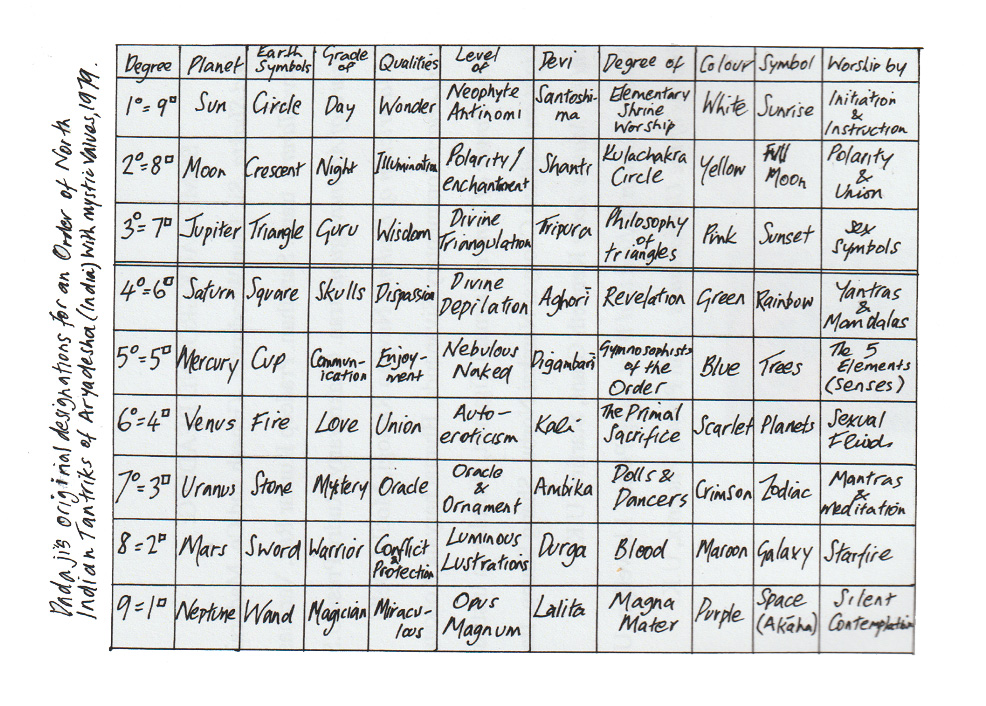
Another elder figure who received one of Dadaji’s grand titles was Dr. Sandy Maclennan, a Scottish psychiatrist. He had worked at Broadmoor Hospital for the criminally insane before retiring to become a general practitioner in Inverness, Scotland. Dadaji dubbed him “Margrave Superia” to “keep an eye on the younger members of the emerging group.” This may have seemed like another attempt to undermine Mike. For a time, things developed quietly, with Sandy and me publishing the first essays on Uttarakaula: Dadaji’s mini Tantras. These were later included in “Nu Tantras” alongside paintings of his chosen Mahavidyas, the Wisdom Goddesses, which represent aspects of the Kaula path and also reflect facets of our consciousness. The early versions of these works were soon integrated into general collections.
Dadaji decided to return to England for several weeks and stayed with other family members who owned land in India, where he had his hermitage. During this time, I had the opportunity to meet him several times in person. One notable occasion was the Guru Purnima gathering, an annual event dedicated to honouring spiritual teachers, which was organized at the house where Dadaji was staying. The event went well.
During the following Guru Purnima, which fell on a summer weekend in Suffolk, several American guests attended. However, Mike returned to London for some reason. While he was away, one of his Nath girls zipped her sleeping bag to mine, and one of the Americans requested initiation into the Uttarakaula tradition. When Mike found out, he reported to Dadaji that I had been stealing his Nath pupils. At one point, Dadaji mentioned that he would like to see the Naths and Uttaras amalgamate; however, he was technically not in a position to formalize this and soon forgot about it anyway.
Dadaji’s next letter to Mike was supposed to include the wonderfully papal expression that I was “excommunicated.” However, after receiving two letters from Sandy and myself, Dadaji began urging me to “stay involved.” I expressed my frustration with the constant squabbling among people who couldn’t rely on his true intentions. Instead, I decided to work with a small local group to focus on researching just one tradition. I continued to keep in touch with Dadaji through Sandy, who consulted him for medical information. Sandy remarked that Dadaji’s brain was like Swiss cheese, full of holes and that those holes were filled with approximations of memories.
I later learned from Muz Murry, who shared letters exchanged between them, that Dadaji was aware of his condition. Indian doctors had informed him that he suffered from a degenerative disease called cervical spondylosis. Muz mentioned that, towards the end, Dadaji could only write in capital letters. Completing a single letter could take him three days, and he experienced impairments in other motor functions as well.
I honoured my commitment to further investigate the Uttarakaula tradition and its associated practices by working with a small local group. While I focused on my art and teaching, our research gradually expanded. This growth was largely facilitated by the advancements in modern communication, in contrast to the old oral traditions that had been traditionally passed down.
Uttarakaula
The Uttarakaulas are part of a Shakti tradition that focuses on the worship of the Goddess. Historically, this tradition has diminished in favour of Shaivite practices, which centre on Shiva, as well as other patriarchal cults that have migrated from northern regions. Originally, there were five Kaula schools, each representing one of the compass directions, along with an additional school representing the quintessence above.
While many practices have been passed down through oral tradition, Kashmiri Shaivism has generated numerous written texts that emphasise the importance of the Goddess in practice. Therefore, when researching this subject, those texts serve as a valuable starting point for expanding knowledge of the Shakta cosmology that Dadaji presented as aspects of the Goddess.
The first notable source from Kashmir is Abhinavagupta, whose works were developed into more accessible forms, such as the comprehensive ‘Tantraloka’ and the summarised version ‘Tantrasara.’ We utilise a form of initiation that combines his writings with the teachings that Dadaji gave me. Other valuable texts include the ‘Kulanava Tantra’ and the ‘Nirruttara Tantra.’ Additionally, I reference general works by Sir John Woodroffe, particularly ‘Shakti and Shakta,’ as well as David Frawley’s ‘Inner Tantric Yoga’ for guidance on mantras and yantras.
Visits to India and Nepal had to wait until later in life than I would have liked but raising young children, and having a father who emigrated to Colorado to get married again at age 73 meant many other things were time-consuming.
What motivated you to write your books, “Nu Tantras of the UttaraKaulas” and “The Rainbow Bridge – The Shakta Tantrika of the Uttarakaulas”?

I named the book Nu Tantras because they were new to Westerners and give a nod to the Egyptian goddess Nuit, with Thelemite significance. Rainbow Bridge is named for Dadaji’s wish to see an East-West fusion bridge of pagan traditions: where Wicca, Thelema and Taoist practices are akin to Tantrika.
Above all, Uttarakaula in Shakti Tantrism is dedicated to the aspects of the nine Mahavidyas, which Dadaji presents as stages of life development, starting from the early Kaula family and continuing into later life, once family responsibilities have been fulfilled. Patriarchal traditions have dominated the world for too long, often restricting women through purdah or worse, creating what Dadaji referred to as the Misery Cults. However, in the last century, especially in the West, domestic technology has played a crucial role in liberating women both socially and intellectually, providing opportunities for spiritual liberation as well.
What advice would you give to someone drawn to Tantra, especially if they come from a different spiritual background like Wicca or Paganism?
”Siva without Shakti is a Shava [a corpse]” and the Kaula lifestyle gives an alternative to the cremation ground of the ascetic waiting for reward posthumously. Shakti and Shakta are two physiological halves of an electric circuit and we enact Shakti and Siva’s union as the deities emerge from our consciousness. Fast male sex is the way of animals. In my experience only when a female partner has reached orgasm is only the beginning of ecstatic transcendence. Males need to prolong their climax by whatever means possible: oral interlude with the partner or repetition aided by the partner for instance. We are in the 21st century, not only do we have the contraceptive bill to do away with caution, but Viagra as well as herbal alternatives. Use them! Pranayama is useful but Tibetan Buddhists withholding ejaculation is not recommended by modern sexologists. It might work for monks but could have psychological and physical damage to offer to casual users.
Once ecstatic levels are achieved, the energy of the Shakti descends from her crown down her spine to her basal chakra, Muladhara. This energy then interacts with the male’s basal chakra and travels up his spine to his crown, creating a continuous circuit.
As with any magical practice, it’s beneficial to document your experiences and visions—whether they are related to the goddess aspect you are channelling or other insights encountered. These notes can aid in self-analysis and can serve as inspirational images for your art, as I have done on canvases and in illustrations for texts. Additionally, they can be utilised in art therapy for enhanced self-realisation.
In India, group practices still exist among certain Kaula clans, despite repression from invading factions, which often leads to secrecy surrounding these practices. They are similar to some Western witches’ Sabbats. Although social attitudes have become more liberal, remnants of old repressions still linger. While there are no fixed patterns for these gatherings, they can range from social rituals to more intimate practices, which tend to occur primarily between established couples. Large groups can lead to disruptive and counterproductive personalities and ideas, so we found that four is an optimal number: one for each element.
Women are naturally drawn to Wicca due to historical suppression, while men tend to be more inclined toward Shaivite organizations, although both genders can participate in mixed-gender activities. The yearly calendar for meetings, which includes solstices, equinoxes, cross-quarter days, and monthly lunar gatherings, does not necessarily align with Indian dates. Therefore, we observe the Wiccan year while also recognizing important Indian dates. For our Green workings, we invoke Pan as the horned god rather than Siva, representing a blend of Western and Eastern traditions. There are few fixed patterns in our practices, and domestic rituals play a significant role in our spiritual unfoldment. Outsiders looking for orgies can find them anywhere but won’t necessarily find them in Tantrika, as there are practices which go way past casual encounters.”
Find more about John’s work and art here at JohnPowerWeb and here, at Uttara Kaula.
In today’s fast-paced world, it is easy to get caught up in the chaos and lose sight of our true selves. This is where The Collective comes in – a group of individuals with a shared passion for spirituality and self-discovery. By following their teachings, we can tap into our inner wisdom and find peace amidst the chaos. The Collective serves as a reminder that sometimes the most powerful guru can be found within ourselves if we are willing to listen. Let us embrace this collective journey towards enlightenment together.

